 WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Feb. 10, 2026) – Applications to fill five seats on the Delta Protection Advisory Committee (DPAC) opened today. The application deadline is 5 p.m. Tuesday, March 31, and the Delta Protection Commission is scheduled to make the appointments May 21.
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Feb. 10, 2026) – Applications to fill five seats on the Delta Protection Advisory Committee (DPAC) opened today. The application deadline is 5 p.m. Tuesday, March 31, and the Delta Protection Commission is scheduled to make the appointments May 21.
The terms of five Committee seats expire in May 2026:
- Delta Organization (Mariah Looney)
- Delta Agriculture Seat 1 (Jeff Iniguez)
- Delta Recreation (vacant)
- State Agency (Edward Hard)
- Utilities-Related Infrastructure (Sam Garcia)
Incumbents are eligible to reapply.
DPAC provides recommendations to the Delta Protection Commission on diverse interests within the Delta, including the Delta’s ecosystem, water supply, socioeconomic sustainability, recreation, agriculture, flood control, environment, water resources, utility infrastructure, and other Delta issues.
Committee members are expected to attend six meetings per year. DPAC typically meets on the first Tuesday of even-numbered months (February, April, June, August, October, and December), though meeting dates may occasionally shift. The 2026 schedule is here. Meetings are held in the Delta at rotating locations.
Committee member terms are three years, so these terms will expire in 2029.
Apply for the openings here.
If you have questions, please contact Delta Protection Commission Executive Director Amanda Bohl at amanda.bohl@delta.ca.gov.

The Delta Protection Commission is hiring a Senior Environmental Planner with responsibilities that are key to the DPC’s mission: land use and levees. If you love rural places and want meaningful opportunities to protect them, this job’s for you.
The DPC’s mission is to protect, maintain, enhance, and enrich the overall quality of the Delta environment and economy. We do this with a focus on agriculture, recreation, and natural resources, while remaining mindful of the importance of the Delta to all Californians.
This Senior Environmental Planner will perform planning, project development, and grants management; conduct analytical studies; formulate procedures and policies; make recommendations to the Executive Director on a broad spectrum of program-related issues that impact the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta; and represent the Commission as assigned.
Occasional travel is required, so candidates must possess a valid driver’s license.
The job is hybrid, requiring at least two days a week of in-person work at the DPC’s office in West Sacramento.
Benefits include:
- Health, dental, and vision insurance,
- CalPERS pension and retirement plans,
- Paid time off and holidays, and
- Professional development opportunities
Requirements: Civil service examination or other proof of eligibility, valid California driver’s license, education transcripts, employment application, Statement of Qualifications
Qualifications: Senior Environmental Planner qualifications can be found on this page
Pay range: $8,678-$10,783/per month
Duty statement: Download PDF
Work location: West Sacramento
Telework: Eligible for remote work, but required to work in office at least two days a week.
Reports to: Executive Director
APPLY BY MARCH 6: Click here for full details and to apply.
Steps to apply:
- Create a CalCareers Account.
- Visit the job announcement at JC-50692 – Senior Environmental Planner and review the Duty Statement (PDF may autodownload; if it does not open, try opening it in a different internet browser.)
- On the Job Control Listing, click Apply Now to launch the CA STD 678, which is the State of California’s official State Application for job vacancies.
- Answer questions/prompts on the CA STD 678 and upload all required documents before submitting the application.
- Verify that the CA STD 678 has been “Submitted” in your CalCareers account.
Other resources for applying for a job with the State:
Department of General Services: How to Apply for a State Job
CalPERS: How to Apply for a State Job
CalCareers: Help
SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Jan. 9, 2026) –Fifteen Delta leaders arrived at Sacramento’s Nature Conservancy on Friday to kickstart their entry into the Delta Leadership Program.
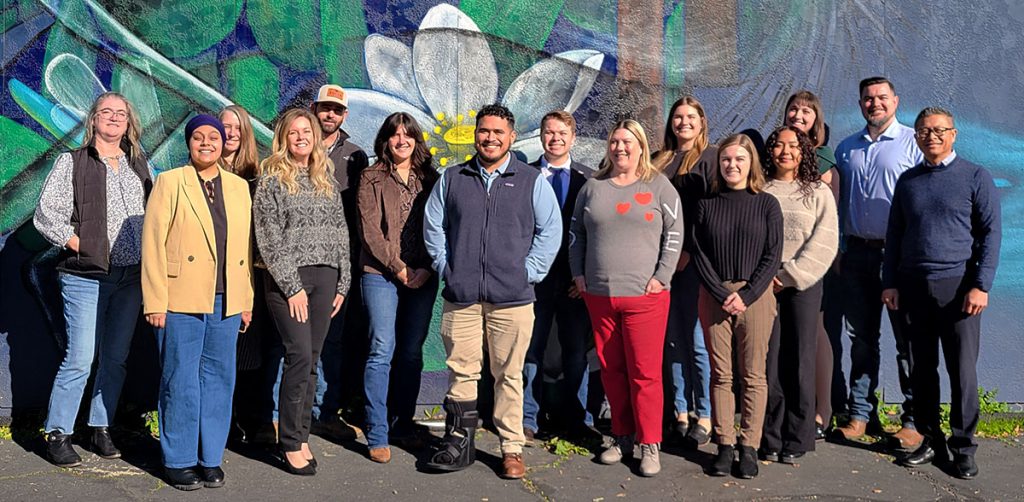

The 2026 Delta Leadership class. Back row L-R: Erin Mullen Brosnan, Rachel Vanderwerff, Jason Culberston, Jack Johnson, Alli Hauger, Nicole Cuellar-Nelson, Bret Bartholomew. Front row L-R: Bhajleen Khalsa, Lisa Kirchhoff, Sabrina Snyder, Gustavo Cruz, Jenni Shaw, Emily Groth, Ashley Castaneda, Minh Nguyen (Photo by Delta Protection Commission/Jada Portillo)
Managed by the Delta Protection Commission and the Delta Leadership Foundation, the program aims to identify potential and emerging leaders in the Delta from an assortment of backgrounds. Over the span of five seminars, participants learn leadership skills and tools to improve and foster community within the Delta.
The first seminar covered an introduction to the Delta, Delta legislation, experiences from alumni of the program, and a panel featuring the three Delta agencies.
This year’s participants are:
- Bret Bartholomew, Owner, Bartholomew Solutions, Elk Grove
- Ashley Castaneda, Restore the Delta, Stockton
- Gustavo Cruz, Assoc. Water Resources Engineer, Solano County Water Agency, West Sacramento
- Nicole Cuellar-Nelson, District Representative, State Senator Christopher Cabaldon, Sacramento
- Jason Culberston, Farmer/Rancher and Trustee, Reclamation District No. 3, Walnut Grove
- Emily Groth, Planner, Contra Costa County Dept. of Conservation and Development, Martinez
- Alli Hauger, Delta Levee Engineer, MBK Engineers, Sacramento
- Jack Johnson, Assistant Deputy, Yolo County Supervisor Oscar Villegas, West Sacramento
- Bhajleen Khalsa, Executive Assistant, State Senator Jerry McNerney, Lathrop
- Lisa Kirchhoff, Co-Owner, Kirchhoff Family Wines, Courtland
- Erin Mullen Brosnan, Board Member and Volunteer, Crockett Historical Society & Museum, Crockett
- Minh Nguyen, Residential Mortgage Lender, F&M Bank, Oakley
- Jenni Shaw, Curator of Education and Visitor Engagement, Lindsay Wildlife Experience. Walnut Creek
- Sabrina Snyder, Senior Management Analyst, Yolo County Administrator’s Office, Woodland
- Rachel Vanderwerff, Senior Environmental Planner, Delta Protection Commission, West Sacramento

The Delta Protection Commission is hiring an Administrative Analyst II to serve as Commission Clerk and become an integral member of our finance and admin team. If you believe in government transparency, love rural places, and want to feel good about the work you do, this job’s for you.
The DPC’s mission is to protect, maintain, enhance, and enrich the overall quality of the Delta environment and economy. We do this with a focus on agriculture, recreation, and natural resources, while remaining mindful of the importance of the Delta to all Californians.
The Clerk works closely with the DPC’s public bodies, including the Commission, the Delta Protection Advisory Committee, and the Delta National Heritage Area Advisory Committee.
The Clerk is responsible for:
- Preparing meeting materials in cooperation with fellow staff members.
- Ensuring all materials are accessible to people with disabilities and posted on the website, in media, and in physical locations in compliance with the Bagley-Keene Act.
- Keeping meetings running smoothly by ensuring a quorum is present and conducting roll call votes.
While much of the work is performed at a computer, attending at least 16 meetings a year gets the Clerk out into a variety of locations in a beautiful rural region rooted in its rivers, dotted with charming legacy communities, filled with farms and wild habitat, and bracketed with urban areas including West Sacramento, Stockton, and the cities of eastern Contra Costa County.
The job is hybrid, requiring three days a week of in-person work at the DPC’s office in West Sacramento.
The ideal candidate will have experience in:
- Accounting and administrative support
- Government functions and public meeting logistics
- Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Office (Word, Outlook, PowerPoint)
- Microsoft Teams and SharePoint
- Document remediation for accessibility
Benefits include:
- Health, dental, and vision insurance,
- CalPERS pension and retirement plans,
- Paid time off and holidays, and
- Professional development opportunities
Requirements: Civil service examination or other proof of eligibility, valid California driver’s license, education transcripts, employment application, Statement of Qualifications
Qualifications: Analyst II qualifications can be found on this page
Pay range: $6,031-$7,547/month
Duty statement: Download PDF
Work location: West Sacramento
Telework: Eligible for remote work, but required to work in office at least three days a week.
Reports to: Staff Services Manager
APPLY BY Feb. 19: Click here for full details and to apply.
Steps to apply:
- Create a CalCareers Account.
- Visit the job announcement at JC-503593 – Administrative Analyst (Analyst II) and review the Duty Statement (PDF may autodownloads; if it does not open, try opening it in a different internet browser.)
- On the Job Control Listing, click Apply Now to launch the CA STD 678, which is the State of California’s official State Application for job vacancies.
- Answer questions/prompts on the CA STD 678 and upload all required documents before submitting the application.
- Verify that the CA STD 678 has been “Submitted” in your CalCareers account.
Other resources for applying for a job with the State:
Department of General Services: How to Apply for a State Job
CalPERS: How to Apply for a State Job
CalCareers: Help
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Nov. 17, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission voted today to appeal the Department of Water Resources’s certification that the Delta Conveyance Project is consistent with the Delta Plan.
The Project would create a 45-mile tunnel starting on the Sacramento River at the town of Hood and ending at the Bethany Reservoir west of Tracy, near the community of Mountain House in the South Delta.
The Commission’s appeal contends that the Project would do lasting harm to the Delta, irrevocably altering “the rural character of the Delta, its economic pillars (agriculture and recreation), and its cultural heritage.”
It also contends that other options that don’t harm the Delta have not been adequately considered.
The project would use thousands of acres of agricultural land during construction and leave another 1,000 permanently changed, often with industrial-looking facilities, at the four major impact areas: Hood, Twin Cities Road near I-5, Lower Roberts Island, and near the Bethany Reservoir State Recreation Area. Other permanent facilities would be built in the Delta on the tunnel route.
The Delta Reform Act of 2009 establishes coequal goals for the Delta of providing a more reliable water supply for California and protecting, restoring, and enhancing the Delta ecosystem. It also states that the coequal goals “shall be achieved in a manner that protects and enhances the unique cultural, recreational, natural resource and agricultural values of the Delta as an evolving place.”
Commissioner Patrick Hume, a Sacramento County Supervisor, said at a preliminary Commission discussion of the matter on Nov. 3: “This body is the the last bastion of support for the Delta as a place. This is really the voice for the flora, the fauna, the farmers, the Flyway, the fisheries, and the economy that the Delta represents.”
The Commission’s vote to appeal on Monday was 9-0, with one abstention.
The Commission is made predominantly of elected representatives in the Delta, with 11 of its 15 members coming from county boards of supervisors, city councils, and local reclamation districts, which are responsible for flood control in the Delta’s low-lying farmland and small communities.
The remaining four members represent state agencies, and they have typically abstained on votes regarding the Delta Conveyance Project.
Commission Chair Diane Burgis, a Contra Costa County Supervisor, did not attend the meeting today and has recused herself from past discussions and votes regarding the Project. Burgis serves on the Delta Stewardship Council, which will hear the Commission’s appeal and any other appeals filed by today’s deadline.
If the Council upholds any of the appeals, the Project could be remanded to DWR to address Delta Plan inconsistencies.
The Commission’s appeal, including maps showing impact areas, can be seen here (PDF).

Amanda Bohl
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Oct. 9, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission has appointed Amanda Bohl as its next Executive Director. She is expected to join the Commission on Oct. 20.
Bohl currently serves on the executive management team of the Delta Stewardship Council, where she is the Special Assistant for Planning and Science. There, she leads the Delta Plan Interagency Implementation Committee (DPIIC) and guides cooperation among the 18 state and federal agencies – including the Delta Protection Commission – involved in the Delta Plan.
Prior to joining the Council in 2016, Bohl was the Economic Development Lead for the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta Conservancy. There, she managed the Delta Marketing Project and helped develop the Conservancy’s Proposition 1 Grant Program, which funded water quality and ecosystem restoration grants.
“The Delta is one of our greatest treasures, rich in natural resources, agriculture, history, and diverse communities,” said Diane Burgis, Chair of the Delta Protection Commission and Contra Costa County’s District 3 Supervisor.
“We were fortunate to have an outstanding pool of candidates. Moving forward, I’m excited about the Delta Protection Commission’s appointment of Amanda Bohl. She brings the vision, leadership, and understanding needed to navigate the complexities of this unique and vital region.”
Bohl has spent her career focused on people’s connection to the land. “When I think of the Delta Protection Commission, I think of landscapes, the land, places,” she said. “I also think of the best of public service and what government can do to protect places.”
She grew up in Amador County, but her childhood was steeped in Delta life. She enjoyed boating and camping in the Delta with her parents and grandparents, and still remembers the family’s drive to Rio Vista in 1985 to see Humphrey the Whale.
“I’m thrilled to be joining the Delta Protection Commission and to be serving the Delta in this new capacity,” Bohl said. “With new challenges and opportunities on the horizon, the Commission’s mission to protect, maintain, enhance, and enrich the overall quality of the Delta environment and economy has never been more important.”
Bohl has a bachelor’s degree in international studies from Southern Oregon University and a master’s degree in community development from the University of California, Davis. She is a 2014 Water Education Foundation Water Leader, and serves on the board of the Sacramento Valley Conservancy.
 Applications are open for the 2026 Delta Leadership Program, a joint effort of the Delta Protection Commission and the Delta Leadership Foundation.
Applications are open for the 2026 Delta Leadership Program, a joint effort of the Delta Protection Commission and the Delta Leadership Foundation.
The program targets potential or emerging leaders in the Delta from all walks of life – agriculture, law enforcement, local government, non-profit organizations, local business, and the tourism and hospitality sectors, among others. It puts participants through an intensive curriculum to expand their knowledge of key issues and challenges in the Delta, teach them leadership skills and tools, build relationships and trust, and foster community.
The ultimate goal of the program, which has been operating since 2016, is to build a cadre of dedicated leaders to protect and improve the Delta. Alumni can be seen in leadership positions throughout the Delta and often appear in the news.
What’s Involved
Interested participants can apply through 5 p.m. Monday, Nov. 24, participants are announced the week of Dec. 8, and the curriculum – five day-long seminars held on Fridays – runs January through April. Applicants must commit to 100% attendance on these dates to be considered for participation in the program:
- Seminar 1: Jan. 9, 2026, in Sacramento
- Seminar 2: Jan. 30, 2026, in Stockton
- Seminar 3: Feb. 20, 2026, in Rio Vista
- Seminar 4: March 20, 2026, in Oakley
- Seminar 5: April 17, 2026, in Clarksburg
In addition to attending seminars, participants work on team projects designed to benefit the Delta, with some of the work occurring during seminars and some on their own time – about two hours per month. Participants also can take an air and water tour of the Delta in March or April, date to be determined.
The program concludes with a graduation at the Delta Protection Commission meeting tentatively scheduled for 5 p.m. May 21 at a location in the Delta. The exact date will be determined in November, when Commission sets its 2026 meeting schedule.
Applying
The application form can be completed online. The deadline is 5 p.m. Monday, Nov. 24, 2025.
The quality and content of the application is critical to the applicant’s success. Try to include specific examples and make sure you have included all of your civic and leadership experience and service.
People accepted into the program will be notified by the week of December 8, 2025.
Submission Checklist
- REQUIRED: Complete the Delta Leadership Program 2026 application form online by 5 p.m. Nov. 24.
- REQUIRED: Upload at least one and up to two substantial letters of recommendation. You will upload these during the online application process.
- OPTIONAL: You may upload your resume during the application process.
QUESTIONS?
If you have questions, please contact Program Coordinator Erik Vink at erik.vink@delta.ca.gov or (530) 650-6327.
 WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (August 5, 2025) – Established by Congress in 2019, the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta National Heritage Area – California’s first and only National Heritage Area (NHA) – is set to be branded and marketed.
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (August 5, 2025) – Established by Congress in 2019, the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta National Heritage Area – California’s first and only National Heritage Area (NHA) – is set to be branded and marketed.
The Delta Protection Commission (DPC) is teaming up with Honey, a design and marketing studio in Sacramento, to create a Tourism Brand and Marketing Plan for the NHA that will promote sustainable tourism and economic development in the region by encouraging responsible use of, and visitation to, the Delta’s unique resources and communities.
“This project is a significant step,” says Program Manager Blake Roberts. “For two decades, we collaborated with our Congressional delegation and the public to establish the NHA. Now we are excited to embark on an important effort that will demonstrate to visitors what a special place the Delta truly is.”
Honey “believes strong branding begins with listening,” says the agency’s president Maggie Hamilton Giordanengo. “We are honored to immerse ourselves in the voices, values, and lived experiences of the Delta communities to craft a brand that inspires sustainable tourism.”
The rollout of the plan will include public outreach, market research and the creation of a brand toolkit. The project is expected to be completed by late June of 2026.
The NHA is managed by the DPC, which is committed to supporting the region’s economic development and the preservation of its historical and cultural significance.
There are 62 National Heritage Areas in the United States. NHAs support historic preservation, natural resource conservation, recreation, heritage tourism, and educational projects through public-private partnerships.
For more information about the Delta NHA Tourism Branding and Marketing plan, contact Kira O’Donnell, NHA information officer, kira.odonnell@delta.ca.gov, (530) 650-6362; or Blake Roberts, NHA program manager, blake.roberts@delta.ca.gov, (530) 650-6572.
For more information about the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta NHA, see our fact sheet (PDF) and the NHA Management Plan (PDF), visit the DPC’s website or call (916) 375-4800.
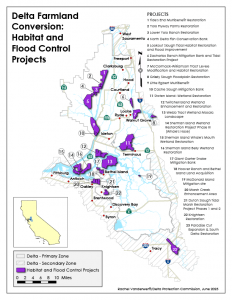 WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (July 24, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission invites public comment through Sept. 8, 2025, on the preliminary report of its study of Delta farmland conversions for water supply, flood control, and habitat projects.
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (July 24, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission invites public comment through Sept. 8, 2025, on the preliminary report of its study of Delta farmland conversions for water supply, flood control, and habitat projects.
Preliminary results of the study (PDF) were presented at public workshops held July 15 and 17, and to the Delta Protection Commission at its regular meeting on July 17. Several speakers highlighted their concern about the impact of the aggregate loss of farmland in the Delta. Agriculture drives the Delta’s economy, and protecting its critical mass is part of the Delta Protection Commission’s mandate.
The research is ongoing, but the Commission is seeking feedback to guide its continuing study. All feedback is welcome, but the DPC is particularly interested in:
- For Delta farmers, reclamation districts, and other landowners, what impacts are they experiencing when farmland is converted?
- Are the processes leading up to the conversions adequate in terms of consultation with adjacent landowners and mitigation of negative impacts?
- Are options to maintain farmland in ways that support ecosystem goals being given adequate consideration?
- Project areas shown on maps in the preliminary report include some acreage that remains as farmland and needs to be subtracted from conversion totals before the research is finalized. Beyond this, is the acreage of completed and planned conversions in the preliminary report accurate and complete?
Comments on the preliminary study may be submitted by email to submit@delta.ca.gov. The deadline is 5 p.m. Monday Sept. 8, 2025.
Wednesday, July 23, 2025, 1:30-2:30 p.m. (end time is approximate)
2101 Stone Blvd, Suite 200
West Sacramento, CA 95691
Pursuant to Government Code section 11123.5, members of the Committee will participate remotely in this meeting. The public will have the same level of remote access.
Password: 699069
Meeting URL: https://us06web.zoom.us/j/89423484620?pwd=AUbfopkGSohxvkbKgbXj8A82b66vwk.1
Join by Telephone
Dial: USA 404 443 6397
USA 877 336 1831 (US Toll Free)
Conference code: 473786
Questions, Comments, and Requests
If you have any questions or have a request for reasonable modification or accommodation due to a disability, please contact the Delta Protection Commission at dpc@delta.ca.gov or (916) 375-4800. Attachments and additional information can be found on the Delta Protection Commission website: delta.ca.gov.
Executive Director Selection Ad Hoc Committee Members
Diane Burgis, DPC Chair, Contra Costa County Board of Supervisors | Oscar Villegas, Yolo County Board of Supervisors | Patrick Hume, Sacramento County Board of Supervisors | Tom Slater, North Delta Reclamation Districts | Gloria Sandoval, CA Natural Resources Agency
 WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Feb. 10, 2026) – Applications to fill five seats on the Delta Protection Advisory Committee (DPAC) opened today. The application deadline is 5 p.m. Tuesday, March 31, and the Delta Protection Commission is scheduled to make the appointments May 21.
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (Feb. 10, 2026) – Applications to fill five seats on the Delta Protection Advisory Committee (DPAC) opened today. The application deadline is 5 p.m. Tuesday, March 31, and the Delta Protection Commission is scheduled to make the appointments May 21.





 Applications are open for the 2026
Applications are open for the 2026  WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (August 5, 2025) – Established by Congress in 2019, the
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (August 5, 2025) – Established by Congress in 2019, the  WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (July 24, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission invites public comment through Sept. 8, 2025, on the preliminary report of its study of Delta farmland conversions for water supply, flood control, and habitat projects.
WEST SACRAMENTO, Calif. (July 24, 2025) – The Delta Protection Commission invites public comment through Sept. 8, 2025, on the preliminary report of its study of Delta farmland conversions for water supply, flood control, and habitat projects.